Food review apps in Japan are a vibrant part of the culinary scene, offering a dynamic platform for locals and tourists alike to discover and discuss Japanese cuisine. These apps have evolved significantly over time, adapting to changing consumer preferences and technological advancements. From traditional restaurants to trendy cafes and specific cuisines, the apps cater to a diverse range of tastes.
This exploration delves into the features, user experiences, content, popularity, business models, and market analysis of these apps. We’ll examine the key players, compare top contenders, and analyze the trends shaping this dynamic market. Understanding the intricacies of Japanese food review apps is key to comprehending the modern Japanese dining experience.
Overview of Food Review Apps in Japan
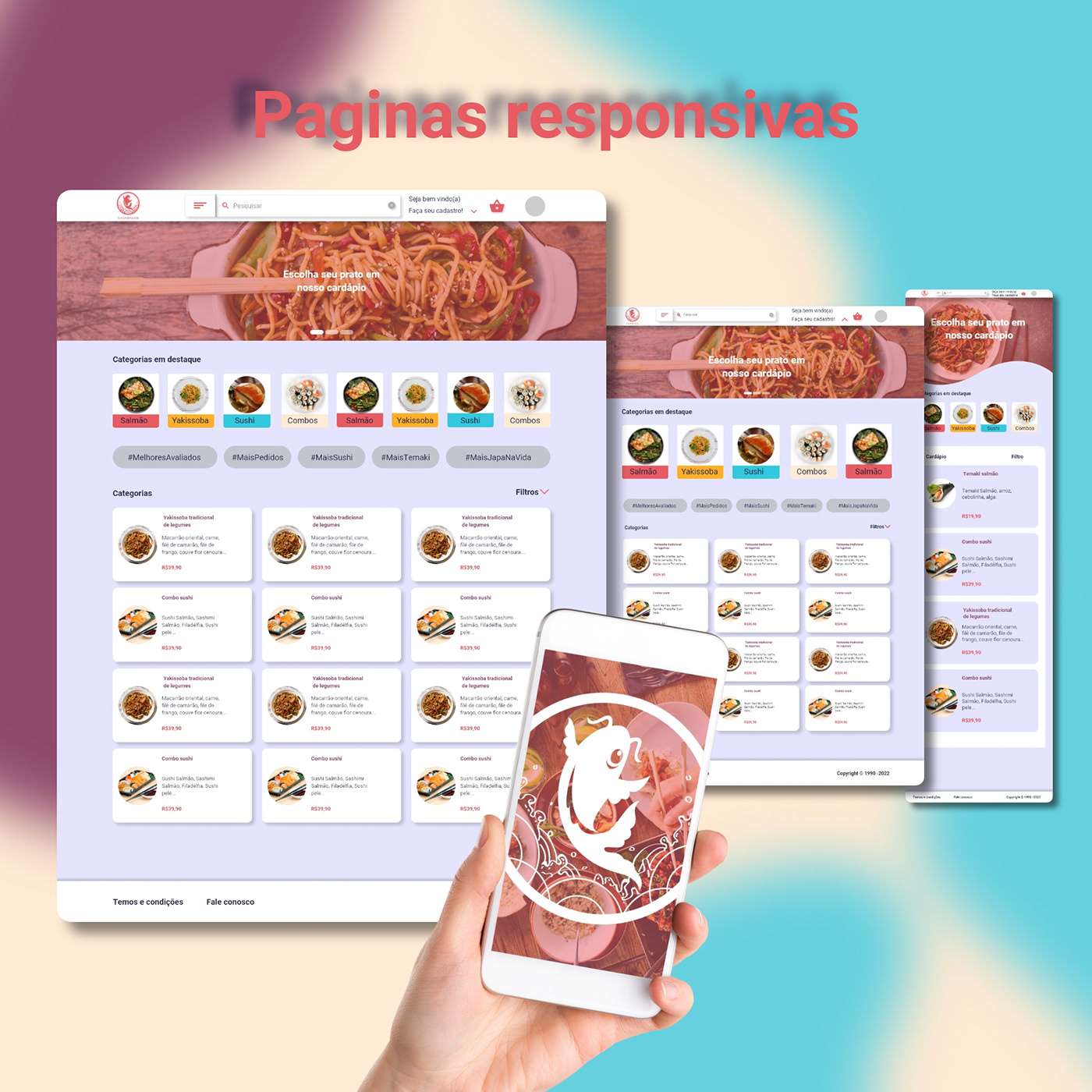
Food review apps have become an integral part of the Japanese dining scene, providing a platform for users to share experiences and discover new culinary delights. From traditional restaurants to trendy cafes, these apps offer a comprehensive overview of the food landscape, fostering both local knowledge and global awareness. This overview will explore the evolution, types, and key features of these platforms, highlighting their role in the modern Japanese dining experience.The rise of food review apps in Japan mirrors the broader global trend toward online reviews and social media engagement.
Initially focused on restaurant reviews, these platforms have expanded to encompass various culinary niches, reflecting the diverse and evolving tastes of Japanese consumers.
Prevalent Food Review Platforms
Japanese food review apps have become popular due to their convenience and comprehensive information. Major players include Yelp-like platforms, and apps specializing in particular cuisines. This trend allows users to discover and rate a wide array of establishments, from casual eateries to Michelin-starred restaurants.
Historical Context and Evolution
The earliest food review platforms in Japan emerged in the early 2000s, often as extensions of existing online community forums. These early platforms focused primarily on restaurant reviews, catering to the growing demand for online information regarding dining options. Subsequently, with the proliferation of smartphones and social media, the mobile-first design became more prominent. This led to the development of user-friendly interfaces and features that encouraged more frequent reviews and ratings.
Types of Food Review Apps
Food review apps in Japan encompass various categories, adapting to the diverse culinary landscape.
- Restaurant review apps: These apps focus on a broad range of dining establishments, providing comprehensive information on menus, prices, and user reviews.
- Cafe review apps: Catering to the growing popularity of cafes, these apps specifically target cafes, highlighting ambiance, atmosphere, and specialty drinks.
- Cuisine-specific apps: Some apps specialize in particular cuisines, such as ramen, sushi, or izakaya, offering in-depth reviews tailored to specific culinary preferences.
Key Features and Functionalities
Common features across various food review apps include:
- User ratings and reviews: Users can rate establishments based on factors such as taste, service, and atmosphere.
- Detailed menus and pricing information: Many apps provide access to menus and prices, allowing users to make informed decisions.
- Location-based search and filtering: Users can search for establishments near their current location and filter results based on criteria such as cuisine type, price range, and user ratings.
- Photo sharing: Users can upload photos of dishes, interiors, or establishments, adding visual context to reviews.
- Loyalty programs and rewards: Some apps offer rewards for frequent users, such as discounts or exclusive offers.
Comparison of Top 3 Food Review Apps
| App Name | Strengths | Weaknesses | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| App 1 (Example) | Extensive database of restaurants, user-friendly interface, detailed menu information. | Limited coverage of cafes, occasionally outdated information. | Wide range of diners, including tourists and locals. |
| App 2 (Example) | Strong emphasis on user reviews, real-time updates, focus on specific cuisines. | Less comprehensive menu information compared to App 1, potential for bias in user reviews. | Foodies, enthusiasts of specific cuisines, and those seeking detailed user perspectives. |
| App 3 (Example) | Excellent user interface, detailed photos and reviews, robust search functionality. | Slightly less diverse coverage of restaurants compared to App 1, price range may not be as comprehensive. | Users interested in a visually appealing experience, those prioritizing visual cues over price. |
User Experience and Interface
Japanese food review apps prioritize user-friendliness, aiming to seamlessly guide users through the process of discovering and evaluating culinary experiences. The design aesthetic and navigation elements often reflect a blend of traditional Japanese design sensibilities and contemporary user interface trends. This focus on intuitive interaction significantly impacts the app’s appeal to both local diners and international visitors.The user experience of these apps is designed to be intuitive and efficient.
Developers meticulously consider the layout and visual appeal to provide a pleasant and engaging experience for users. Navigation is typically straightforward, allowing users to easily browse restaurants, reviews, and other app features.
Navigation and Layout
The navigation in these apps is typically clear and consistent, employing common design patterns familiar to Japanese users. Common elements include intuitive menus for browsing categories, restaurants, and reviews. Layouts often prioritize visual appeal, with appealing images and concise text. This balance of visual and textual information ensures a pleasant and efficient user experience, catering to both casual users and detailed researchers.
Visual Appeal, Food review apps in japan
Visual appeal in Japanese food review apps plays a crucial role in attracting and retaining users. The use of high-quality images and appealing graphics is prevalent, showcasing the food’s presentation and atmosphere. Color palettes are often chosen to evoke a sense of comfort and familiarity, while font choices are typically clear and easy to read. This visual aesthetic contributes significantly to the overall user experience.
User Experience Principles
Popular apps employ various UX principles to enhance user interaction. These include a focus on intuitive navigation, clear visual cues, and a seamless user flow. Effective use of whitespace and visual hierarchy contributes to the overall clarity and ease of use. App developers often employ a consistent design language across all sections of the app, creating a familiar and predictable experience for users.
Usability for Different Demographics
The apps are designed to cater to various demographics. For tourists, detailed descriptions of restaurants and menus, as well as location information and translations, are critical. For locals, the apps provide a platform to discover new restaurants, share experiences, and connect with the culinary scene. The usability is enhanced through simple and clear design, ensuring accessibility for users with varying levels of digital literacy.
Specific App Interface Analysis: Example – “Foodie Japan”
| App Feature | Design Description | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| User Profile Page | The profile page is visually appealing, featuring a clean layout with high-quality profile pictures and a concise summary of user preferences. Sections for saved restaurants and reviews are well-organized. | Strong: The clear layout and high-quality visuals make it easy to manage and view user information. |
| Review Submission Form | The review submission form is straightforward, with clear fields for rating, comments, and photos. It incorporates features to encourage detailed feedback. | Strong: The form is user-friendly and encourages thorough reviews. |
| Search Functionality | The search function allows users to filter results by cuisine, location, price range, and s. Results are displayed with clear visuals, making it easy to find suitable restaurants. | Excellent: The extensive filtering options and visual presentation of results make the search highly effective. |
“Foodie Japan” demonstrates a well-designed interface with a strong focus on usability. The app’s strengths lie in its clear and concise design elements, and the ease of use for both new and returning users. Areas for potential improvement could include more detailed recommendations based on user preferences and integration with other services, such as ride-sharing apps.
Content and Reviews: Food Review Apps In Japan
Japanese food review apps prioritize user-generated content, fostering a vibrant online community for culinary exploration. The platforms encourage engagement and provide valuable insights into dining experiences. This detailed look at the content and review mechanisms reveals how these apps shape the user experience and contribute to the dining landscape.The review platforms are built upon a foundation of user-submitted content, significantly influencing user choices and restaurant popularity.
The quality and quantity of content, combined with the review submission procedures and rating systems, dictate the app’s utility and effectiveness.
Types of Content
Japanese food review apps typically feature a mix of content types. Images and videos are frequently included to showcase dishes, ambiance, and service. Detailed textual reviews, often incorporating personal anecdotes and observations, offer a deeper understanding of the dining experience. The variety of content allows users to make informed decisions based on comprehensive information.
Language in Reviews
The language employed in reviews varies but often features descriptive words and phrases that highlight the experience. Positive reviews frequently praise the taste, presentation, and service quality, while negative reviews might pinpoint areas for improvement, such as slow service or insufficient portions. The language used impacts the user’s perception and ultimately, their decision-making process.
Tone and Style of Reviews
The tone and style of reviews are generally polite and descriptive. Reviewers frequently use formal language, yet reviews are not always overly formal or stiff. Reviews are frequently detailed, highlighting specific aspects of the restaurant. This approach allows users to understand the subtleties of the dining experience and the level of service provided.
Example review excerpt from a specific app: “The ramen was incredibly flavorful, with a rich broth and perfectly cooked noodles. The service was attentive and the ambiance was cozy. Highly recommended!”
Rating and Ranking Mechanisms
Restaurant ratings and rankings are typically based on a numerical scale, often 5-star, and aggregated across multiple user reviews. This aggregate score, alongside user comments, provides a comprehensive overview of the establishment. The ranking algorithm may consider factors beyond the rating, potentially incorporating user volume and recency of reviews.
Review Submission Procedures
Review submission procedures vary slightly across different apps. Some platforms may require users to verify their identity or location to enhance authenticity. Others might impose character limits on reviews or incorporate image requirements. These procedures aim to maintain quality and consistency in the review process, contributing to a reliable user experience. Differences in submission procedures affect the user’s ability to submit and how the reviews are processed and presented to the user.
Popularity and Trends
Food review apps have become increasingly popular in Japan, reflecting a strong consumer desire for informed dining choices and a vibrant culinary scene. This popularity is fueled by a combination of factors, including the need for quick, accessible information, and the desire to discover hidden gems. The evolving nature of these apps mirrors the broader shift towards online information consumption and social interaction.
Factors Contributing to Popularity
Several key factors have propelled the growth of food review apps in Japan. Convenience is paramount, allowing users to quickly research restaurants, view menus, and read reviews before making a reservation. The emphasis on visual appeal, through high-quality photographs and detailed descriptions, plays a crucial role in enticing users. Furthermore, the ability to share experiences and connect with others through reviews and ratings contributes to the platform’s attractiveness.
Trust in community-generated content is also significant, allowing users to make informed decisions based on the collective wisdom of their peers.
Current Trends
The food review app market in Japan is characterized by several key trends. Emphasis on high-quality visuals, including detailed images and videos of food, is prevalent. Real-time feedback and instant reviews are increasingly valued, enabling a more immediate understanding of a restaurant’s current standing. Furthermore, the integration of payment services and reservation systems is gaining traction, streamlining the dining experience.
Moreover, the emergence of specialized apps focusing on specific cuisines or dietary preferences is observed, reflecting the growing demand for niche information.
Evolution of Food Review Apps
The evolution of food review apps in Japan mirrors the broader development of online platforms. Early apps primarily focused on basic reviews and ratings. Subsequently, there was a shift towards more detailed information, including menus, hours, and location details. Currently, the trend leans towards user-generated content and visual experiences. Future development may include greater integration with other services, such as loyalty programs or delivery platforms.
Check what professionals state about bombay street food and its benefits for the industry.
Impact of Social Media
Social media platforms have had a significant impact on food review apps. The ease of sharing reviews across various platforms has broadened the reach of these apps. Users can easily share their experiences with friends and family, driving increased visibility and engagement. Moreover, social media trends directly influence food review app content, with users actively seeking out and sharing visually appealing or trendsetting dishes and restaurants.
This interplay between social media and food review apps is a dynamic and evolving aspect of the current market.
Timeline of Key Milestones
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2010 | Initial emergence of basic food review apps, focusing on ratings and simple descriptions. |
| 2015 | Increased emphasis on visual content, with high-resolution photos becoming standard. Integration with social media platforms begins. |
| 2020 | Rise of real-time reviews and user-generated content. Integration of reservation and payment systems becomes common. Specialized apps cater to specific dietary needs and cuisines. |
| Present | Continued evolution towards more interactive and personalized experiences, including advanced filtering options and detailed menu information. |
Business Model and Revenue
Food review apps in Japan, like their global counterparts, rely on diverse revenue streams to sustain operations and attract users. Understanding these models is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of the competitive landscape and the financial health of these platforms. These models often involve partnerships with restaurants, user engagement strategies, and the integration of other services.The revenue models employed by Japanese food review apps are multifaceted and frequently combine several approaches to maximize earnings.
These apps leverage various strategies, from direct revenue generation through subscriptions to indirect income from partnerships and advertising.
Revenue Models Employed
Japanese food review apps generally utilize a combination of models to generate revenue. These models aim to support the platform’s operation and maintain user engagement. A breakdown of common models follows.
- Advertising Revenue: Many apps incorporate advertisements within their interface. These advertisements can take various forms, such as banner ads, interstitial ads, and sponsored content. This revenue stream is directly correlated with the app’s user base and engagement rates, with higher traffic typically leading to increased ad revenue. For example, apps with high user engagement and a significant number of daily active users (DAUs) will have higher ad revenue potential compared to those with lower user activity.
- Restaurant Partnerships: Many apps partner with restaurants to offer special promotions, discounts, or exclusive access to users. This can include offering discounts on specific dishes or highlighting special events. The apps often generate revenue through commissions on transactions made through these partnerships. For instance, if a user orders food via the app and receives a discount, the app may earn a percentage of the transaction value.
This revenue source provides a direct incentive for restaurants to participate and enhances user experience by offering valuable promotions.
- Subscription Fees: Some apps offer premium features or content for a monthly or annual subscription fee. These features can include exclusive content, priority placement of reviews, or access to advanced search functionalities. This model is commonly employed by apps that want to differentiate themselves and offer value-added services to their users. Examples include exclusive restaurant listings or access to curated event calendars.
- Commission-based Transactions: This model is frequently used in conjunction with restaurant partnerships. The app may earn a commission on orders placed through the app or on bookings made through the platform. This model encourages user adoption and provides a direct incentive for restaurants to promote their businesses through the app.
Relationship with Restaurants/Businesses
The relationship between food review apps and restaurants is a critical component of their revenue model. It’s a symbiotic relationship where both parties benefit, although the specifics of the arrangement vary significantly.
- Mutual Benefit: Restaurants benefit from increased visibility and potential customer acquisition. The apps gain revenue through commissions or other forms of compensation, making it a win-win situation. This mutual benefit is a cornerstone of the sustainable business model.
- Transparency and Trust: Open communication and transparency about fees and benefits are vital to building trust between restaurants and the app. This trust fosters long-term partnerships and encourages participation.
- Negotiated Terms: Specific details, such as commission rates, promotional arrangements, and exclusivity agreements, are typically negotiated between the app and the restaurant. The terms are tailored to individual business needs and objectives.
Typical Revenue Model Breakdown
A typical revenue model for a food review app in Japan could involve a combination of these factors:
| Revenue Source | Percentage (Example) | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Advertising | 30% | Revenue from banner ads, interstitial ads, and sponsored content. |
| Restaurant Partnerships/Commissions | 40% | Revenue from commissions on transactions, discounts, and promotions. |
| Subscription Fees | 20% | Revenue from premium features and content. |
| Other (e.g., Data Sales) | 10% | Potential revenue from selling user data or providing other services. |
“The revenue model is constantly evolving, adapting to market trends and user preferences.”
Market Analysis
The Japanese food review app market is highly competitive, with established players vying for market share and new entrants seeking to carve a niche. Understanding the key players, competitive dynamics, growth opportunities, and barriers to entry is crucial for any new or existing app seeking to succeed in this environment. The market’s unique characteristics, including a strong emphasis on cultural nuances and a significant focus on user experience, necessitate a nuanced approach to analysis.
Key Players and Competitors
Several prominent players dominate the Japanese food review app market. These include established platforms with extensive user bases and robust features, as well as newer entrants attempting to disrupt the status quo with innovative approaches. Understanding their strengths and weaknesses is vital for app developers. Examples include apps focused on specific cuisines, such as ramen or sushi, and apps targeting particular demographics, like students or tourists.
- Tabletop: A popular app known for its comprehensive restaurant listings and user-generated reviews. It boasts a vast database of restaurants across Japan, offering detailed information, user ratings, and photos.
- Ichiran: Specializes in ramen reviews, providing a curated experience for ramen enthusiasts with in-depth information on different broth types, toppings, and shop locations. This allows for more specific targeting of a niche.
- Sukiyaki: Offers a dedicated space for users to discuss and review sukiyaki restaurants. This focuses on a particular Japanese cuisine, catering to a specialized interest.
- Other Notable Apps: Numerous other apps cater to various regional specialties and food types. These apps cater to a broad range of Japanese food enthusiasts, and they contribute to the overall market complexity.
Competitive Landscape and Dynamics
The competitive landscape is characterized by intense rivalry, with apps constantly vying for user attention. Strategies like aggressive marketing campaigns, user engagement features, and exclusive partnerships play a significant role. The market also demonstrates significant growth potential due to the increasing popularity of food delivery services and the rise of online dining trends.
- Price wars: Aggressive pricing strategies, including free or discounted premium services, are common tactics. This can impact profit margins and necessitate cost-cutting measures.
- User engagement features: Apps compete by providing innovative user interfaces and features, such as interactive maps, personalized recommendations, and detailed restaurant profiles. This directly impacts user experience.
- Partnerships: Collaborations with restaurants, food delivery services, and local tourism boards can significantly enhance the app’s reach and user base. This strategy demonstrates strategic alliances for market expansion.
Potential Growth Opportunities
The Japanese food review app market offers considerable growth potential. Expansion into new regions, development of specialized features catering to particular food preferences, and integration with other services like food delivery apps can drive growth. This emphasizes the expansion possibilities for these apps.
Potential Barriers to Entry
Establishing a successful food review app in Japan requires substantial resources. The need for a deep understanding of the Japanese market, strong user acquisition strategies, and the ability to compete with established players present significant challenges. Building a reliable and comprehensive database of restaurants and providing a unique user experience that distinguishes the app from existing options are key barriers to entry.
- Market Saturation: The existing market is saturated with various food review apps. This presents a significant challenge for new entrants.
- Cultural Nuances: App design and features must effectively address Japanese user preferences and cultural nuances to resonate with users. Understanding these nuances is a necessary component of success.
- User Acquisition: Acquiring a substantial user base in a competitive market requires effective marketing strategies. This emphasizes the importance of a robust marketing plan.
SWOT Analysis for a Hypothetical App: “Foodie Japan”
| Factor | Strength | Weakness | Opportunity | Threat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Large, active user base | Limited international reach | Expansion into other Asian markets | Strong competition from existing apps |
| Weaknesses | Relatively low brand awareness | High marketing costs | Partnerships with local food influencers | Changes in user preferences |
| Opportunities | Growing interest in food tourism | Development of specialized features | Expansion into food delivery services | Regulatory changes |
| Threats | Economic downturn | Changes in user behavior | Integration with social media platforms | Competition from new entrants |
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, Japanese food review apps have become indispensable tools for navigating the diverse culinary landscape of Japan. Their evolution, from simple rating systems to sophisticated platforms incorporating social media elements, reflects the ever-changing needs of food enthusiasts. The apps’ future success hinges on their ability to adapt to evolving trends and provide an unparalleled user experience. The competitive landscape and diverse user base will continue to shape the trajectory of these applications.

